Nexus-e
Interconnected Energy System Modeling Platform
Contact: Dr. Blazhe Gjorgiev
Policy changes in the energy sector result in wide-ranging implications throughout the entire energy system and influence all sectors of the economy. Due partly to the high complexity of combining separate models, few attempts have been undertaken to model the interactions between the components of the energy-economic system.
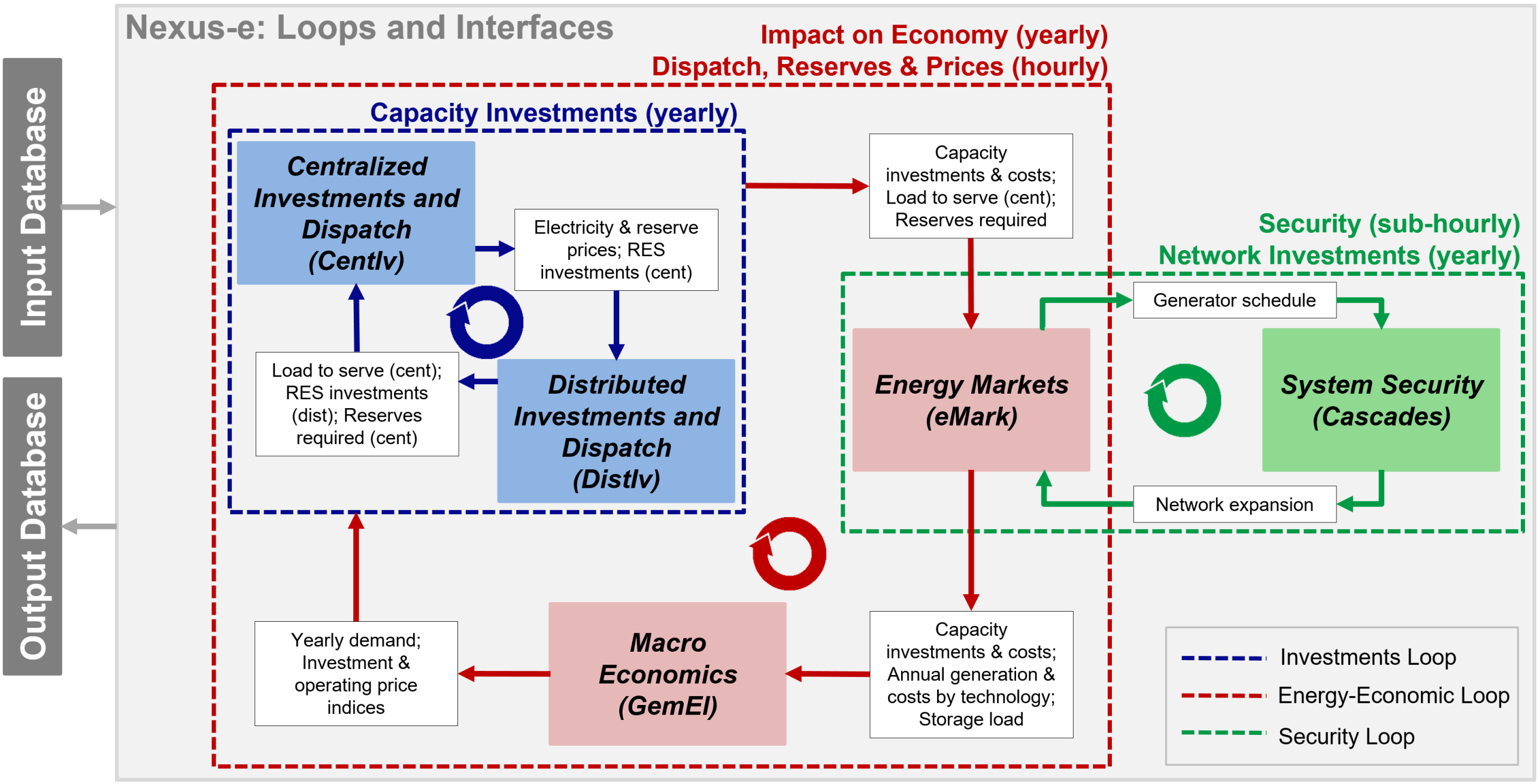
The Nexus-e Interconnected Energy Systems Modeling Platform aims to fill this gap by providing an interdisciplinary framework of modules that are linked through well-defined interfaces to holistically analyze and understand the impacts of future developments in the energy system. This platform combines bottom-up and top-down energy modeling approaches to represent a much broader scope of the energy-economic system than traditional stand-alone modeling approaches. The Nexus-e platform is featured with its modularity, defined interfaces, and transparency.
The Nexus-e platform consists of five interlinked modules:
- General Equilibrium Module for Electricity (GemEl): a computable general equilibrium (CGE) module of the Swiss economy,
- Centralized Investments Module (CentIv): a grid-constrained generation expansion planning (GEP) module considering system flexibility requirements,
- Distributed Investments Module (DistIv): a GEP module of distributed energy resources,
- Electricity Market Module (eMark): a market-based dispatch module for determining generator production schedules and electricity market prices,
- Network Security and Expansion Module (Cascades): a power system security assessment and transmission system expansion planning module.
The five core modules of Nexus-e focus on the Swiss Electricity System. The core modules include four bottom-up high-resolution electricity system modules and one top-down economic module. By interconnecting the modules, the Nexus-e platform accounts for energy demand and supply, macro energy-economic factors, and energy policy drivers across multiple time-scales and levels of aggregation.
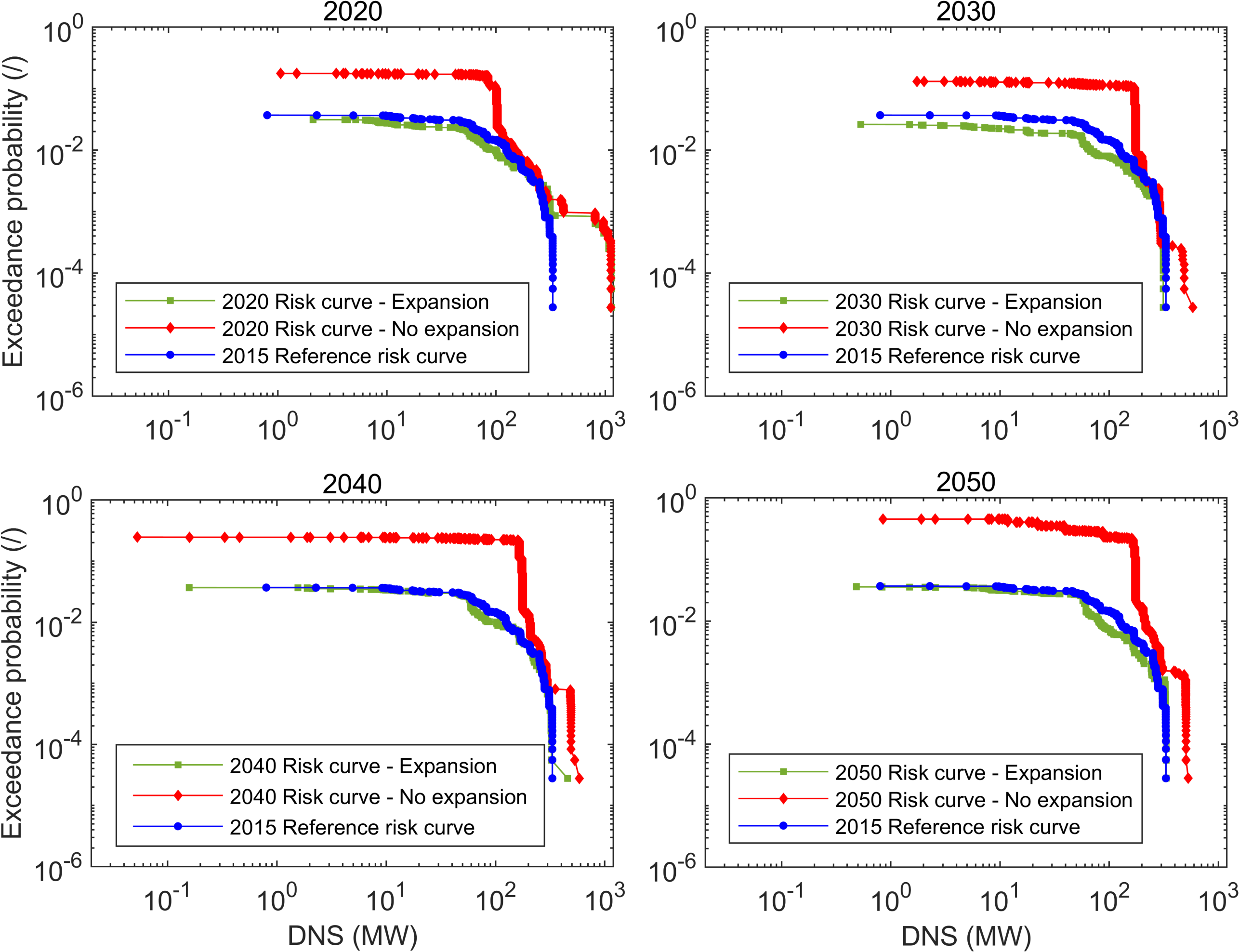
The RRE laboratory is developing the Cascades module. The Cascades module aims to: (1) assess the security of supply by testing the capability of a power system to withstand sudden changes, i.e. due to component failures; and (2) to provide a transmission system expansion plan if a target level of security is not satisfied. The Cascades module comprises two models, a cascading failure simulations model and a transmission system expansion planning model.